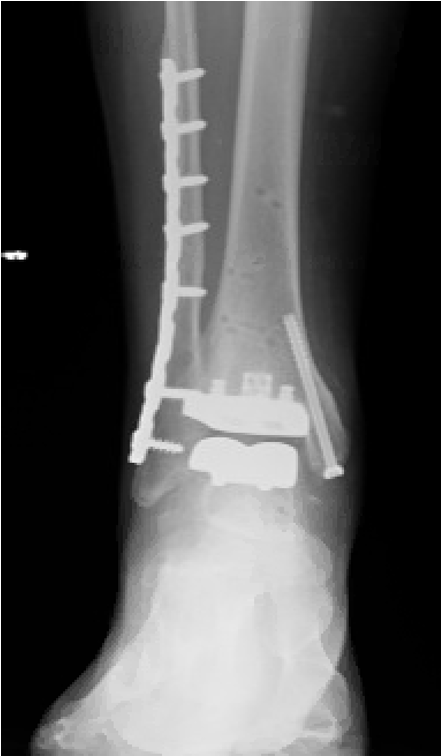
Total ankle replacement
Background
Ankle arthritis is a condition that can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the ankle joint. It is most commonly seen in older adults from chronic wear and tear, but can also occur in younger people who have had previous ankle injuries or rheumatologic disease. Ankle arthritis can greatly impact a person's quality of life and ability to perform daily activities.
The symptoms of ankle arthritis can include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the ankle joint. These symptoms can worsen over time, making it difficult to walk or participate in physical activities. In severe cases, the ankle joint may become deformed or lose range of motion.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ankle arthritis is made by an orthopedic foot and ankle surgeon with a physical exam and X-rays. Sometimes a CT scan or MRI can also help determine the extent of joint damage and the severity of the arthritis.
Nonsurgical management
Nonsurgical management is often the first line of treatment for ankle arthritis. This may include lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, exercise, and avoiding high-impact activities that exacerbate symptoms. Physical therapy and the use of orthotics or braces can also be helpful in relieving pain and improving mobility.
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, a walking boot or ankle brace help to provide additional support and stability to the ankle joint.
Surgical management
When nonsurgical management of ankle arthritis fails to provide relief, surgery can be considered. Two common surgical options for ankle arthritis are ankle fusion and ankle replacement.
In ankle fusion, the bones of the ankle joint are made to grow together. This eliminates the joint motion, which in turn eliminates the source of pain. Ankle fusion is a highly effective procedure for relieving pain caused by ankle arthritis, but it inhibits ankle mobility. After an ankle fusion, patients typically have a stable, pain-free ankle for walking and low impact activities, but they may have difficulty with certain activities such as jogging or stairs.
Ankle replacement, also known as ankle arthroplasty, involves replacing the damaged ankle joint with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic components. The technology of ankle replacement is evolving quickly and it offers the advantage of preserving ankle mobility and more natural gait. Ankle replacement is not suitable for all patients, as there is a risk of implant failure or need for revision surgery.
““With the fusion, . . . it actually is better support. Like if I have to go up a curb or something, I can bear weight on it better. . . . You feel like it’s more stable”
...It [the TAR] just reacts like . . . your normal ankle. . . . The fusion doesn’t turn anywhere; you have to pick it [up] and move”
People who have been through these surgeries have been described how they feel in the scientific study “Living With Both a Total Ankle Replacement and an Ankle Fusion”. Both ankle replacement and ankle fusion have risks and benefits. The choice of surgical treatment depends on several factors, including the severity of the arthritis, the patient's age and activity level, and their personal preferences. Seek out evaluation with an orthopedic foot and ankle specialist with experience in both techniques to determine the best option for you.
In summary, ankle arthritis is the cause of significant pain and mobility issues, but you don’t have to live with it. With proper diagnosis and individualized management, you can improve your quality of life and function.